
Step 2: Fix a common difference and add or subtract from the first term to get the second term. Step 1: Take a starting number that will act as the first term of the AP. If you want to make an AP, then follow these steps: For instance, if we have an arithmetic sequence :ĭ = ( t x – t x-1), where ‘t’ refers to the term and ‘x’ = 2, 3, 4, 5, …… The common difference ‘d’ can be calculated by subtracting the next term from the previous term.
#ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE FORMULA HOW TO#
How to Find the Common Difference between an AP Hence the algebraic sequence is an arithmetic sequence. Thus each term has a common difference of 2 between them. Now let us look at the algebraic sequence.Hence this series is not an arithmetic sequence. Here as you can see, the difference between two consecutive terms is changing from -3 to -2 to -4. Therefore series 1 is an arithmetic progression. You can see that every time two terms are being subtracted, the answer comes as 4. So why are these APs? It can be understood by seeing the common difference between each series term. Given below are some series that are arithmetic progression:


Don’t get confused and understand that it means an arithmetic progression. You can find a lot of different examples where the abbreviation will be given.
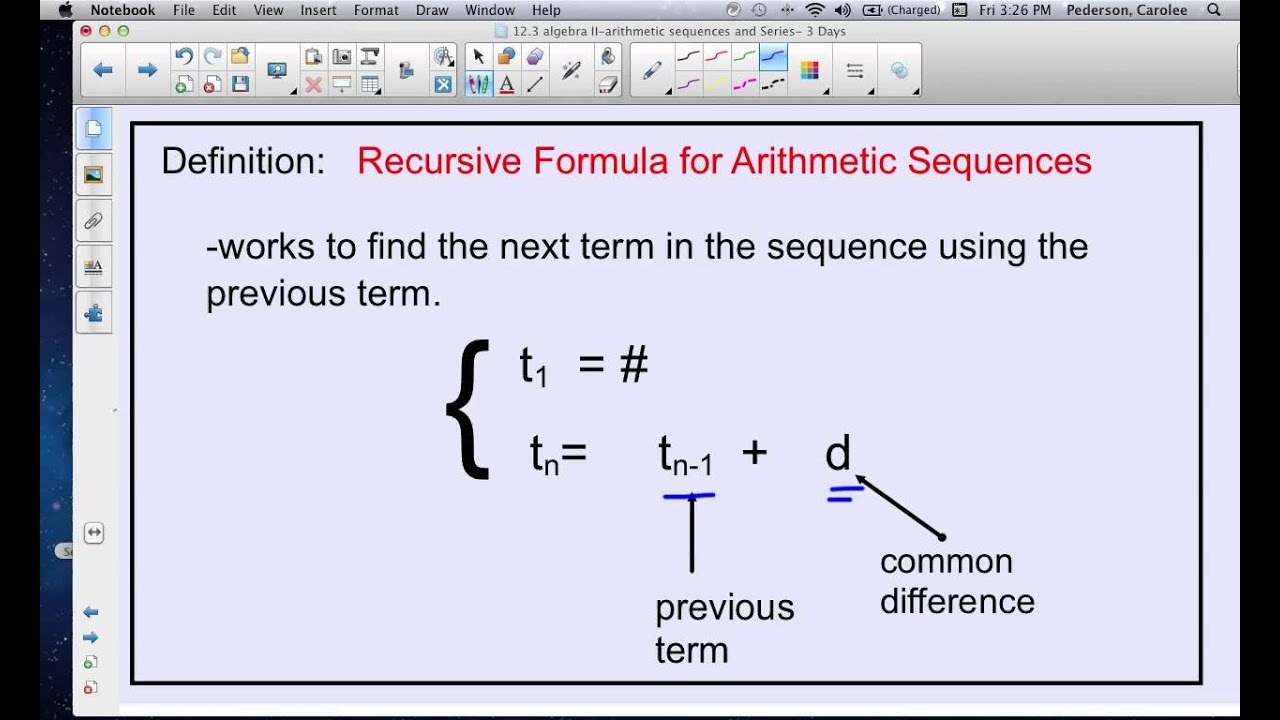
We can concur that if the numbers in a list increase or decrease with a constant common difference, they are in an arithmetic sequence or arithmetic progression.Īrithmetic Progression or arithmetic sequence is also denoted by ‘AP’. This difference is known as the common difference and is denoted by the letter ‘d’. An arithmetic sequence or arithmetic progression is defined as a sequence of integers where the difference between any two numbers is always constant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
